Understanding Blood Glucose Monitoring
Understanding Blood Glucose Monitoring

Blood glucose monitoring is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes, helping individuals maintain their blood sugar levels within a target range. This practice is essential for people with type 1 diabetes and those who take insulin, but it can also benefit anyone managing diabetes.
Why Monitor Blood Glucose?
Monitoring blood glucose levels helps you understand how your body responds to various factors such as diet, exercise, and medications. By keeping track of these levels, you can make informed decisions about your diabetes management plan. Regular monitoring can help prevent complications associated with high or low blood sugar levels, such as heart disease, nerve damage, and vision problems
How to Monitor Blood Glucose
There are two primary methods for monitoring blood glucose levels:
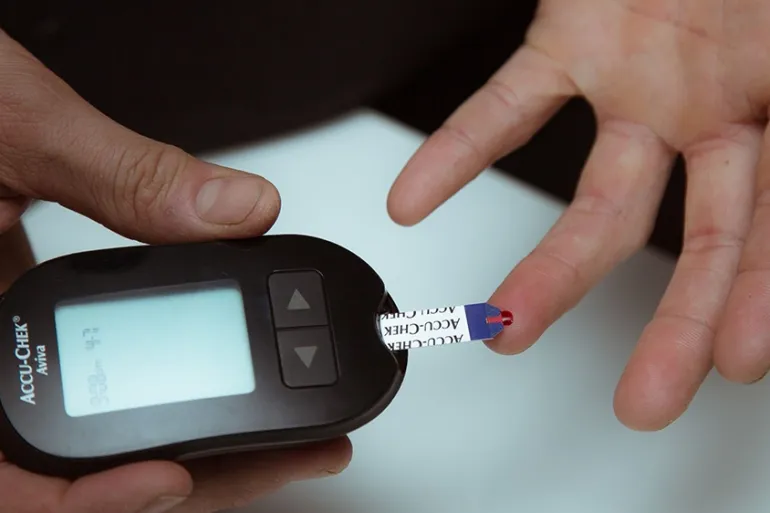
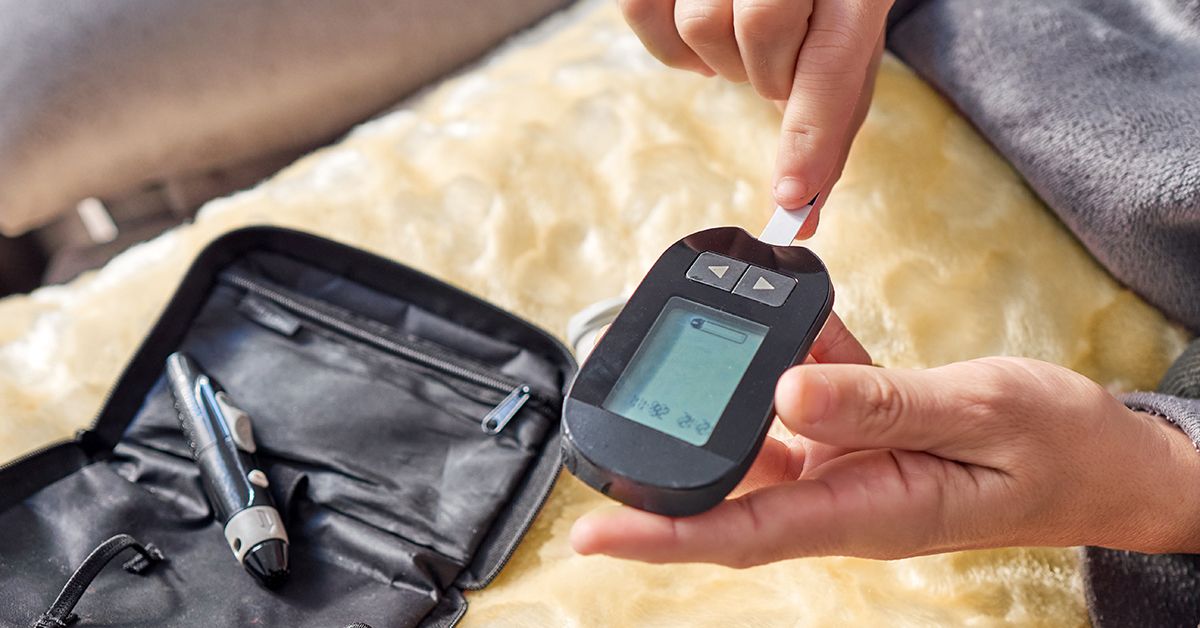
- Glucometer: This device uses test strips to measure the glucose level in a small blood sample, usually obtained from a finger prick. It’s a quick and straightforward method that provides immediate results.
- Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM): A CGM system uses a sensor placed under the skin to continuously measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. It provides real-time data and alerts for high or low blood sugar levels
When to Monitor Blood Glucose
The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on your diabetes management plan. Your healthcare provider will guide you on how often to check your levels. Common times to test include:
- Before and after meals
- Before and after exercise
- Before bedtime
- When you feel symptoms of high or low blood sugar
Understanding Your Results
Interpreting your readings is vital for effective diabetes management. Here are some general target ranges:
- Fasting (before meals): 80-130 mg/dL
- Postprandial (1-2 hours after meals): Less than 180 mg/dL
These ranges can vary based on individual health conditions and goals, so it’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations
Benefits of Blood Glucose Monitoring
Regular monitoring offers several benefits:
- Improved Diabetes Management: Helps you make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
- Prevention of Complications: Reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications by maintaining blood sugar levels within the target range.
- Personalized Care: Allows for adjustments in your diabetes management plan based on real-time data
Conclusion
Blood glucose monitoring is a powerful tool in managing diabetes effectively. By understanding your blood sugar levels and how they respond to different factors, you can take proactive steps to maintain your health and well-being. Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring plan for your needs.