2024 OSCE Implementation: Subdural Haematoma
2024 OSCE Implementation: Subdural Haematoma
Subdural haematomas are a critical condition that healthcare professionals must manage effectively. The 2024 updates to the Nursing and Midwifery Council’s (NMC) Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) emphasize evidence-based practices, making it essential for nursing professionals to stay informed about the latest guidelines and treatment protocols for subdural haematomas.
Understanding Subdural Haematoma
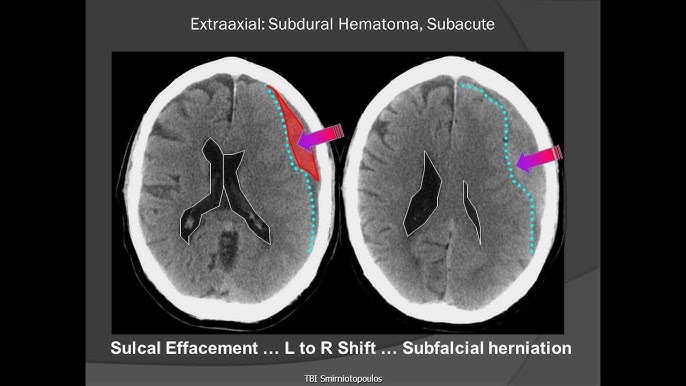
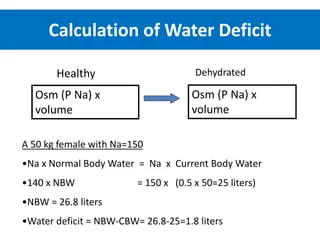
A subdural haematoma is a collection of blood between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater of the brain. This condition typically results from head trauma, which causes blood vessels to rupture and bleed into this space. Subdural haematomas can be acute, subacute, or chronic, depending on the timing of symptom onset after the injury
Importance of Evidence-Based Practice in Subdural Haematoma Management
The NMC OSCE assesses the clinical competence of nurses and midwives who wish to practice in the UK. The inclusion of subdural haematoma scenarios in the OSCE highlights the importance of evidence-based practice in managing this serious condition. The 2024 updates to the OSCE introduce new scenarios and marking criteria that emphasize accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and patient-centered care
Evidence-Based Guidelines for Subdural Haematoma Management
Research and clinical guidelines provide a framework for the effective management of subdural haematomas. Key evidence-based practices include:
- Assessment and Diagnosis: Conduct a thorough neurological assessment to determine the severity of the haematoma. Use imaging techniques such as CT scans to confirm the diagnosis
- Initial Treatment: Stabilize the patient by managing airway, breathing, and circulation. Administer medications to reduce intracranial pressure if necessary.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases of significant haematoma, surgical intervention such as craniotomy or burr hole drainage may be required to relieve pressure on the brain
- Postoperative Care: Monitor the patient closely for signs of increased intracranial pressure and other complications. Implement a rehabilitation plan to support recovery.
- Patient Education: Educate patients and their families about the condition, treatment options, and the importance of follow-up care.
Implementing Effective Subdural Haematoma Management in OSCE
To effectively manage a subdural haematoma in the OSCE, nurses should:
- Perform a Comprehensive Assessment: Evaluate the patient’s history, conduct a physical and neurological examination, and use appropriate diagnostic tools.
- Apply Evidence-Based Treatment: Implement initial stabilization measures and consider surgical options if necessary.
- Develop a Postoperative Care Plan: Create a personalized care plan that includes monitoring and rehabilitation.
- Communicate Clearly with Patients and Families: Explain the diagnosis, treatment plan, and expected outcomes. Encourage questions and provide clear instructions for home care.
Conclusion
The 2024 updates to the NMC OSCE underscore the importance of evidence-based practice in the management of subdural haematomas. By adhering to the latest guidelines and incorporating patient-centered care, nurses can ensure effective treatment and optimal outcomes for patients with subdural haematomas. Staying informed about current best practices and continuously improving clinical skills will be essential for success in the OSCE and in everyday clinical practice.