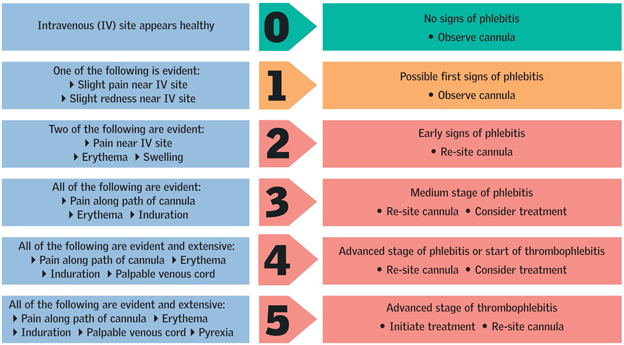
How to Perform Correct A to E Assessment for the NMC OSCE
How to Perform Correct A to E Assessment for the NMC OSCE

The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) is a vital step for overseas nurses aiming to practice in the UK. One of the critical components of the OSCE is the A to E assessment, which ensures a systematic approach to evaluating and managing acutely unwell patients. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you master this essential skill.
Step 1: Airway (A)
Start by assessing the patient’s airway to ensure it is clear and unobstructed.
- Check for Obstructions: Look for any visible obstructions in the mouth or throat.
- Listen for Sounds: Listen for any abnormal sounds like stridor or gurgling, which may indicate an obstruction.
- Ask the Patient: If the patient is conscious, ask them to speak. Difficulty speaking can indicate airway issues.
Step 2: Breathing (B)
Next, assess the patient’s breathing to ensure they are getting adequate oxygen.
- Observe: Look for chest rise and fall, and note the rate, rhythm, and depth of breathing.
- Listen: Use a stethoscope to listen to breath sounds on both sides of the chest.
- Measure: Check the respiratory rate and oxygen saturation levels using a pulse oximeter.
Step 3: Circulation ©
Evaluate the patient’s circulation to ensure adequate blood flow and perfusion.
- Pulse Check: Assess the pulse for rate, rhythm, and strength.
- Blood Pressure: Measure the patient’s blood pressure.
- Capillary Refill: Check capillary refill time by pressing on a fingernail and observing how quickly color returns.
- Look for Signs of Shock: Pale, clammy skin and altered mental state can indicate poor circulation.
Step 4: Disability (D)
Assess the patient’s neurological status to identify any disabilities.
- Level of Consciousness: Use the AVPU scale (Alert, Voice, Pain, Unresponsive) to assess consciousness.
- Pupil Response: Check the pupils for size, equality, and reaction to light.
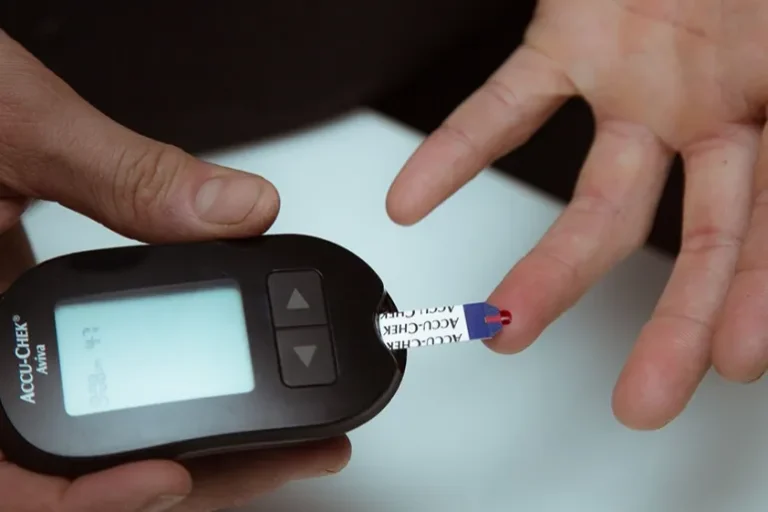
- Glucose Levels: Measure blood glucose levels if the patient shows signs of altered mental status.
Step 5: Exposure (E)
Finally, expose the patient to complete a thorough examination while maintaining their dignity and privacy.
- Inspect the Body: Look for any signs of injury, rashes, or other abnormalities.
- Temperature: Measure the patient’s body temperature.
- Maintain Warmth: Ensure the patient is kept warm and covered as much as possible to prevent hypothermia.
Tips for Success
- Stay Systematic: Follow the A to E sequence methodically to ensure no step is missed.
- Communicate Clearly: Explain each step to the patient to keep them informed and reassured.
- Document Findings: Record all observations and measurements accurately for further evaluation.
By following these steps, you can perform a correct A to E assessment efficiently and accurately, ensuring patient safety and meeting the NMC OSCE standards.