2024 Pressure Ulcer Prevention: OSCE Evidence-Based Practice
2024 Pressure Ulcer Prevention: OSCE Evidence-Based Practice

Understanding Pressure Ulcers
Pressure ulcers can develop quickly and are often challenging to treat. They typically occur in areas where the bone is close to the skin, such as heels, elbows, hips, and the base of the spine. The primary risk factors include immobility, poor nutrition, moisture, and decreased sensory perception.
The Role of OSCE in Pressure Ulcer Prevention
The OSCE is a practical exam used to assess the clinical skills of healthcare professionals. For those working in environments where pressure ulcers are a risk, the OSCE ensures that practitioners can apply evidence-based practices effectively. The exam typically includes scenarios that test your ability to assess, prevent, and manage pressure ulcers.
Key Evidence-Based Practices for Pressure Ulcer Prevention
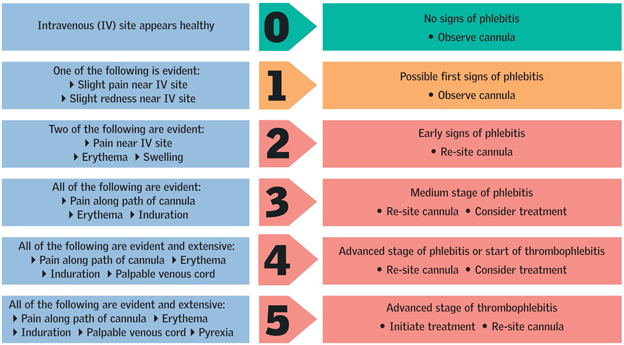
- Risk Assessment: Regularly assess patients for their risk of developing pressure ulcers using validated tools like the Braden Scale. Early identification of at-risk patients is crucial1.
- Skin Inspection: Conduct daily skin inspections, focusing on bony prominences. Look for early signs of pressure damage, such as redness or discoloration2.
- Repositioning: Frequently reposition patients to alleviate pressure on vulnerable areas. The recommended frequency is at least every two hours3.
- Support Surfaces: Use specialized mattresses and cushions that redistribute pressure. These can significantly reduce the risk of pressure ulcer development4.
- Nutrition and Hydration: Ensure patients receive adequate nutrition and hydration. Malnutrition and dehydration can increase the risk of pressure ulcers5.
- Moisture Management: Keep the skin dry and clean. Use barrier creams and manage incontinence to prevent moisture-related skin damage6.
Preparing for the OSCE
To excel in the OSCE, it is important to:
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of the latest research and guidelines on pressure ulcer prevention.
- Practice Scenarios: Engage in mock OSCE scenarios to build confidence and improve your clinical skills.
- Reflect on Feedback: Use feedback from practice sessions to identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
The 2024 OSCE for Pressure Ulcer Prevention emphasizes the importance of evidence-based practices in providing high-quality care. By understanding and applying these practices, healthcare professionals can significantly reduce the incidence of pressure ulcers and improve patient outcomes.