2024 Subcutaneous Injection: NMC OSCE Evidence-Based Practice
2024 Subcutaneous Injection: NMC OSCE Evidence-Based Practice
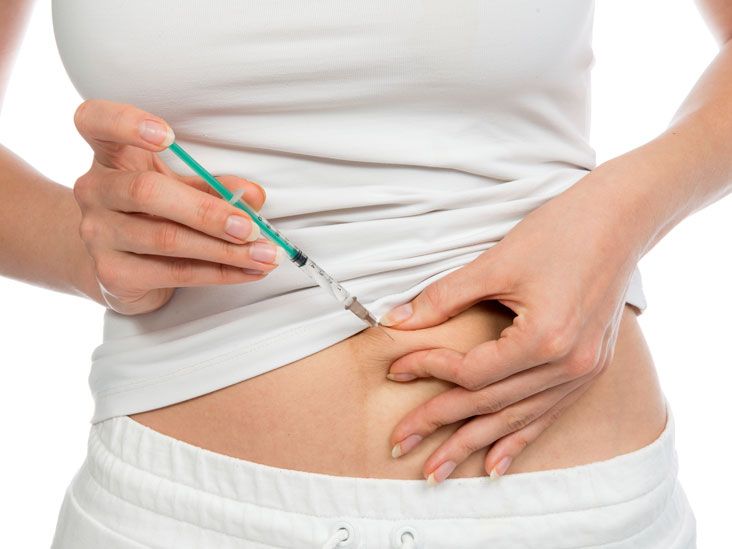
Subcutaneous injections are a fundamental skill in nursing practice, and their correct administration is crucial for patient safety and effective treatment. The 2024 updates to the Nursing and Midwifery Council’s (NMC) Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) emphasize evidence-based practices, making it essential for nursing professionals to stay informed about the latest guidelines and techniques for subcutaneous injections.
Understanding Subcutaneous Injections
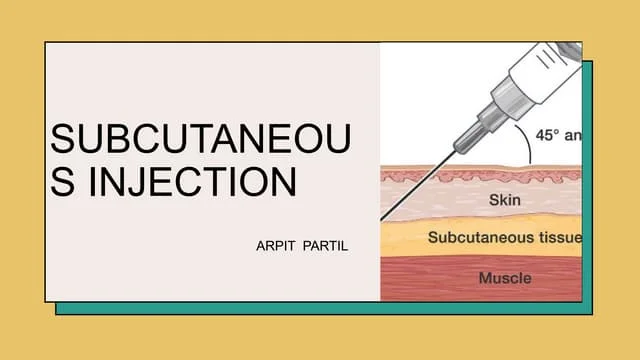
A subcutaneous injection involves administering medication into the tissue layer between the skin and the muscle. This route is commonly used for medications that require slow, sustained absorption, such as insulin and anticoagulants. Proper technique is vital to ensure the medication is delivered effectively and to minimize discomfort and complications for the patient.
Importance of Evidence-Based Practice in Subcutaneous Injection
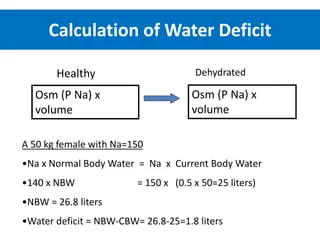
The NMC OSCE assesses the clinical competence of nurses and midwives who wish to practice in the UK. The inclusion of subcutaneous injection scenarios in the OSCE highlights the importance of evidence-based practice in performing this common procedure. The 2024 updates to the OSCE introduce new scenarios and marking criteria that emphasize the need for precision, patient-centered care, and adherence to best practices12.
Evidence-Based Guidelines for Subcutaneous Injection
Research and clinical guidelines provide a framework for the effective administration of subcutaneous injections. Key evidence-based practices include:
- Preparation: Ensure all necessary equipment is prepared and the medication is correctly dosed. Verify the patient’s identity and check for any allergies.
- Site Selection: Choose an appropriate injection site, such as the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. Rotate sites to prevent tissue damage and ensure consistent absorption.
- Technique: Use a clean, non-touch technique to prevent infection. Pinch the skin to create a fold and insert the needle at a 45 to 90-degree angle, depending on the needle length and the patient’s body type.
- Injection: Inject the medication slowly and steadily. Withdraw the needle at the same angle you inserted it and apply gentle pressure to the site with a sterile gauze.
- Documentation: Record the details of the injection, including the medication, dose, site, and any patient reactions.
Implementing Effective Subcutaneous Injection in OSCE
To effectively perform a subcutaneous injection in the OSCE, nurses should:
- Perform a Comprehensive Assessment: Evaluate the patient’s history, conduct a physical examination, and confirm the medication order.
- Apply Evidence-Based Technique: Follow the guidelines for preparation, site selection, and injection technique.
- Communicate Clearly with Patients: Explain the procedure, address any concerns, and provide aftercare instructions.
- Document the Procedure: Ensure accurate and thorough documentation of the injection and any patient responses.
Conclusion
The 2024 updates to the NMC OSCE underscore the importance of evidence-based practice in the administration of subcutaneous injections. By adhering to the latest guidelines and incorporating patient-centered care, nurses can ensure effective treatment and optimal outcomes for patients. Staying informed about current best practices and continuously improving clinical skills will be essential for success in the OSCE and in everyday clinical practice.