2024 Restraints: Evidence-Based Practice (OSCE)
2024 Restraints:Evidence-Based Practice (OSCE)
Introduction
In the realm of healthcare, ensuring patient safety while maintaining dignity is paramount. The use of physical restraints, though sometimes necessary, must be approached with caution and guided by evidence-based practices. This blog delves into the 2024 guidelines for restraint use in clinical settings, particularly focusing on the Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) for nurses.
Understanding Restraints
Physical restraints are devices or methods used to limit a patient’s movement. They are typically employed to prevent harm to the patient or others. However, their use is controversial and must be justified by clinical evidence and ethical considerations.
Evidence-Based Practice in Restraint Use
- Assessment and Justification:
- Before applying restraints, a thorough assessment is crucial. This includes evaluating the patient’s physical and mental state, understanding the underlying causes of their behavior, and exploring alternative interventions
- Use restraints only after less restrictive measures have failed and you have a clear, documented rationale.
- Types:
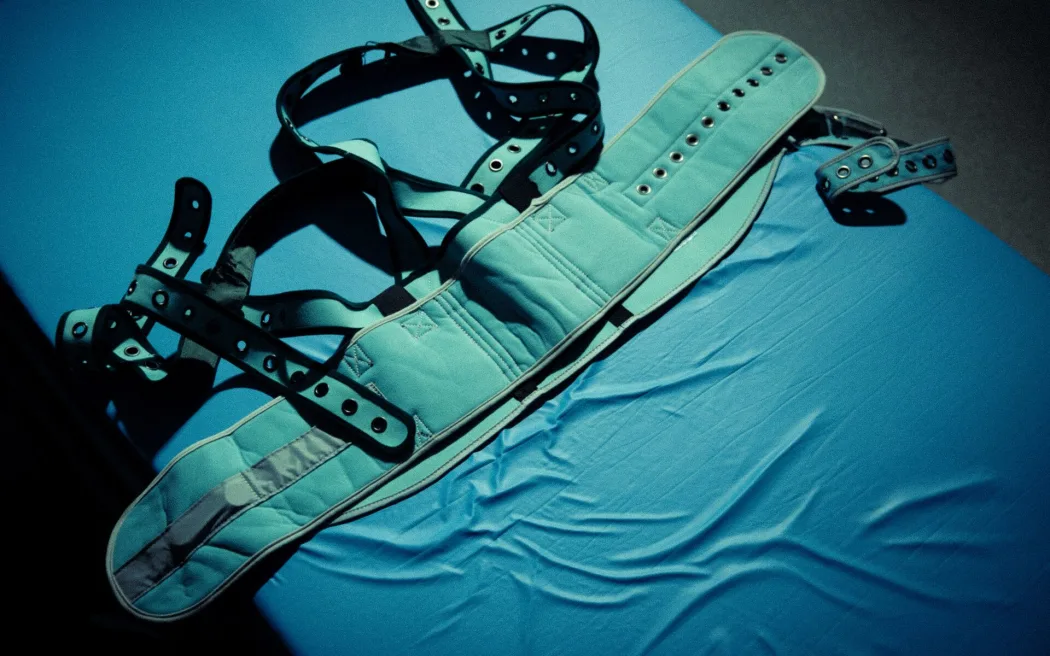
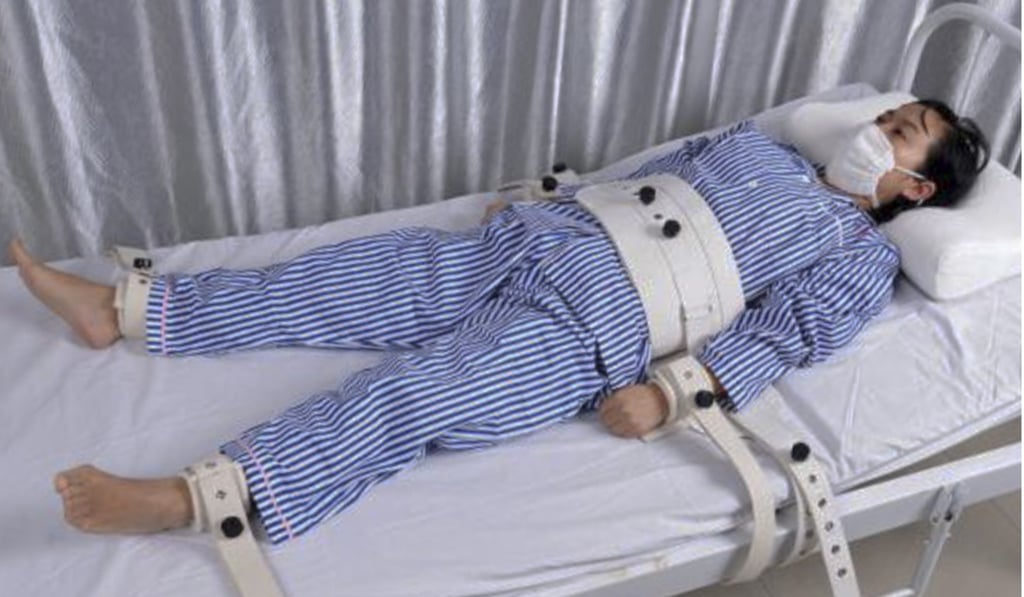
- Physical Restraints: These include belts, straps, or garments designed to restrict movement.
- Chemical Restraints: Medications used to control behavior or restrict freedom of movement.
- Environmental Restraints: Modifications to the patient’s surroundings to limit mobility.
- Guidelines for Use:
- Informed Consent: Whenever possible, obtain informed consent from the patient or their legal representative.
- Regular Monitoring: Patients under restraint must be monitored continuously to ensure their safety and comfort. Regular checks should be documented.
- Duration and Documentation: They should be used for the shortest duration necessary. Detailed documentation of the reason for restraint, duration, and patient response is essential
OSCE and Restraint Practices
The OSCE is a critical component of nursing education and certification. It assesses the practical skills and knowledge of nurses in a controlled environment. When it comes to restraint use, the OSCE evaluates:
- Knowledge of Guidelines: Understanding the latest evidence-based guidelines and ethical considerations.
- Practical Skills: Demonstrating the correct application of restraints, ensuring patient safety, and maintaining dignity.
- Communication: Effectively communicating with patients, families, and healthcare teams about the need for it and obtaining consent.
Conclusion
The use of restraints in healthcare is a delicate balance between ensuring safety and respecting patient autonomy. By adhering to evidence-based practices and guidelines, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions that prioritize patient well-being. The OSCE plays a vital role in preparing nurses to handle these challenging situations with competence and compassion.